Understanding DRS in Cricket: A Comprehensive Guide

Cricket, a sport rich in tradition and history, has evolved significantly over the years. One of the most notable advancements in the modern game is the introduction of technology to assist in decision-making. The Decision Review System (DRS) is a prime example of this technological integration. This article delves into the intricacies of DRS, exploring its origins, components, impact on the game, and the controversies it has sparked.
The Origins of DRS
The Decision Review System was introduced to address the human errors that can occur in umpiring decisions. Cricket, being a game of fine margins, often sees decisions that can change the course of a match. The International Cricket Council (ICC) first trialed DRS in 2008 during a Test series between India and Sri Lanka. The system was officially launched in 2009, with the aim of reducing umpiring errors and increasing the accuracy of decisions.
Components of DRS
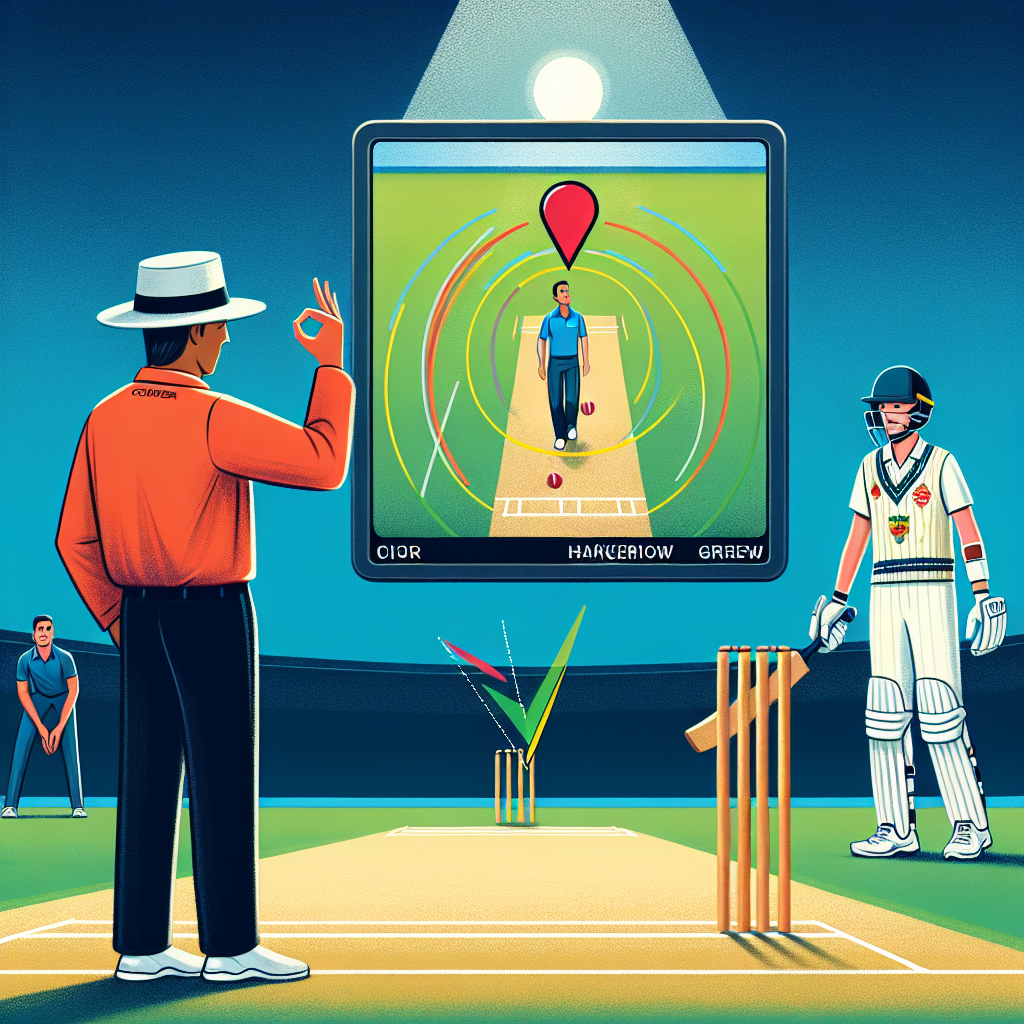
DRS is a complex system that combines several technologies to assist umpires in making accurate decisions. The main components include:
- Hawk-Eye: A ball-tracking technology that predicts the path of the ball after it has been bowled. It is primarily used for LBW (Leg Before Wicket) decisions.
- UltraEdge/Snickometer: An audio-visual tool that detects the sound of the ball hitting the bat or pad. It is crucial for determining whether a batsman has edged the ball.
- Hot Spot: An infrared imaging system that highlights the point of contact between the ball and the bat or pad. It is used to confirm edges and bat-pad catches.
How DRS Works
DRS is initiated by the players, not the umpires. Each team is allowed a limited number of unsuccessful reviews per innings, which varies depending on the format of the game. The process involves the following steps:
- The fielding team or the batsman can challenge an on-field umpire’s decision.
- The third umpire reviews the decision using the available technology.
- The third umpire communicates the final decision to the on-field umpires, who then inform the players.
Impact of DRS on Cricket
DRS has had a profound impact on cricket, influencing both the players and the spectators. Some of the key impacts include:
Increased Accuracy
DRS has significantly improved the accuracy of umpiring decisions. According to ICC statistics, the accuracy rate of decisions has increased from around 90% to 98% with the use of DRS. This has led to fairer outcomes and reduced controversies on the field.
Strategic Element
DRS has added a new strategic dimension to the game. Teams must use their reviews judiciously, balancing the risk of losing a review against the potential gain of overturning a crucial decision. This has added an extra layer of intrigue to the game.
Viewer Engagement
The use of technology in DRS has enhanced viewer engagement. Fans enjoy the suspense and drama that comes with a review, as well as the opportunity to see the technology in action. This has made cricket broadcasts more interactive and entertaining.
Controversies and Criticisms
Despite its benefits, DRS has not been without controversy. Some of the criticisms include:
Technology Limitations
While DRS aims to reduce errors, it is not infallible. Technologies like Hawk-Eye and UltraEdge have their limitations, and there have been instances where the technology has failed to provide conclusive evidence. This has led to debates about the reliability of DRS.
Inconsistency in Implementation
There have been inconsistencies in how DRS is implemented across different series and tournaments. Some boards have opted not to use certain technologies due to cost or logistical reasons, leading to a lack of uniformity in the system.
Player Reactions
DRS has also affected player behavior. Some players have been criticized for using reviews as a tactical tool rather than for genuine errors. This has raised questions about the spirit of the game and the integrity of the review process.
Case Studies: Memorable DRS Moments
Over the years, DRS has been at the center of several memorable moments in cricket. Here are a few notable examples:
2011 World Cup: Sachin Tendulkar’s LBW
During the 2011 World Cup semi-final between India and Pakistan, Sachin Tendulkar was given out LBW by the on-field umpire. However, he reviewed the decision, and Hawk-Eye showed the ball missing the stumps. The decision was overturned, and Tendulkar went on to score a crucial 85 runs.
2019 Ashes: Ben Stokes’ Miracle at Headingley
In the third Test of the 2019 Ashes series, Ben Stokes played one of the greatest innings in Test history. With England needing two runs to win and one wicket remaining, Stokes was given out LBW. He reviewed the decision, and Hawk-Eye showed the ball missing the stumps. The decision was overturned, and Stokes led England to a remarkable victory.
The Future of DRS
As technology continues to advance, the future of DRS looks promising. The ICC is constantly exploring new technologies to enhance the system, such as real-time ball tracking and improved audio-visual tools. The goal is to make DRS more accurate, consistent, and accessible to all cricket-playing nations.
Conclusion
The Decision Review System has revolutionized cricket, bringing greater accuracy and fairness to the game. While it has its limitations and controversies, the benefits of DRS are undeniable. As the system continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of cricket. For players, umpires, and fans alike, DRS represents a significant step forward in the quest for a more just and exciting game.
In summary, DRS has transformed cricket by reducing umpiring errors, adding strategic depth, and enhancing viewer engagement. Despite its challenges, it remains a vital tool in modern cricket, ensuring that the game is played in the true spirit of fairness and competition.